The odds are stacked against property owners in Las Vegas, where the commercial real estate market continues to suffer from a severe downturn. With nearly $17.2 billion in distressed assets across all commercial property types, Las Vegas ranks No. 1 among U.S. metros by proportion of distress to total inventory in the local market, according to New York-based Real Capital Analytics.
Some analysts suggest the volume of troubled commercial loans could create a wave of foreclosures similar to those that swept through the residential market, a specter that is eroding confidence in commercial real estate. Meanwhile, the pool of available buyers has shrunk and the return on investment they require has increased, depressing sale prices.

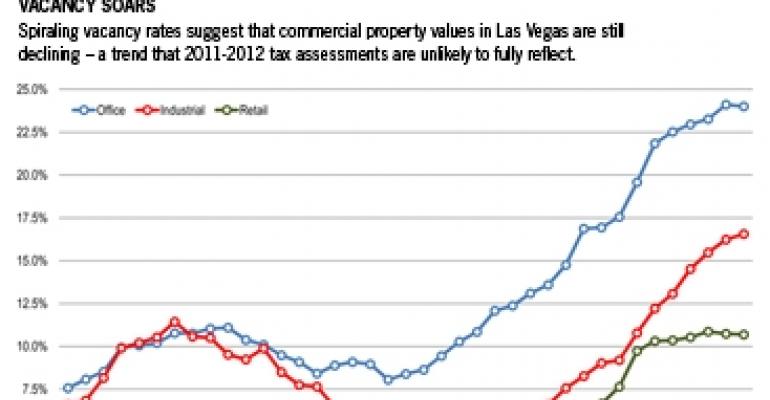
Vacancy rates are another metric that illustrates the severity of the downturn. The vacancy rate for all classes of office space in Las Vegas has slowed its rate of increase, but is projected to top out at a staggering 24.8% by the end of this year, according to Encino, Calif.-based real estate services firm Marcus & Millichap. By contrast, the firm estimates that the current, national vacancy rate for all classes of office is 17.7%.
Applied Analysis, a research consulting firm based in Las Vegas, reports that vacancy rates have risen for the past four years in every subsector of commercial real estate, from retail to industrial to office. The average price per acre of developable commercial land in Clark County has fallen from a peak of $939,000 at the end of 2007 to $155,000 today, a drop of more than 83%, according to Applied Analysis.
Brian Gordon, a principal at the research company, draws a direct correlation between the weak demand for space and the depressed value of commercial properties.
The cumulative effect of these trends is clear: The market value of commercial property has dramatically declined. The question that remains for property owners is whether the taxable values assessors assign to Las Vegas real estate will reflect the decline in market value. Unfortunately for taxpayers, the short answer is no.
Data lag skews values
During any period of changing real estate values, Nevada’s taxable property assessments tend to fall out of step with the current market. The tendency to reflect outdated property values doesn’t mean the staff of the assessor’s office isn’t keeping up with the latest newspaper headlines. Rather, it’s because assessors are required to follow a methodology that doesn’t reflect recent shifts in market value.
In Nevada, the assessor is required to adhere to a valuation methodology that, in the current market, is biased toward a value that will exceed market value. To begin with, the sales data assessors use to establish pricing is simply outdated.
Nevada tax law requires assessors to value the land and improvement components of an improved parcel separately. The land component is valued by comparing it to the sale of vacant land. The comparable transactions are drawn from sales that occurred six months to three years prior to the valuation date, a point in time when real estate was selling for higher prices than is the case today.
In a market in which values are rising, the reliance on “old” sales data would tend to result in a taxable value that is below market value. In a declining market, however, the reliance on old sales will tend to result in a taxable land value that exceeds market value.
A different problem derives from assessors’ methodology for valuing the improvement component of a property. In Nevada, improvements are valued according to replacement cost, or what it would cost to build a duplicate asset today, less depreciation.
Replacement cost is established from cost manuals published by Los Angeles-based Marshall & Swift, which monitors materials pricing for the commercial and residential real estate industries.
Reliance on replacement cost may be relevant in a market that is not overbuilt. But in a market with excess inventory, the replacement cost of a building will not reflect economic obsolescence that makes the space less marketable to tenants, and therefore less valuable.
The appraisers in the Clark County Assessor’s office currently are valuing properties for the tax year that begins on July 1, 2011 and runs to June 30, 2012. More likely than not, the methodology they are required to follow will result in taxable values that exceed market value.
If that occurs, the assessor is required to reduce taxable value to market value. As a practical matter, however, it is unlikely the reduction to market value will be made because the assessor’s office simply does not have the time or property-specific information on vacancy, rent and expenses to determine the market value of all commercial properties. That limitation puts the onus on the property owner. Taxpayers will receive a notice of the taxable value assigned to their property for tax year 2011-2012 in early December. Even if that taxable value is less than the value it was assigned in the preceding tax year, the bias in the methodology employed by the assessor is likely to have resulted in a taxable value that still exceeds market value.
Owners must ask themselves what a snapshot of their property’s market value would be on Jan. 1, 2011. If the market trends previously described continue, any reasonable level of analysis is likely to support a market value for most commercial properties that is less than the taxable value determined by the assessor.
Consequently, owners of most commercial properties in Las Vegas will have good reason to appeal to the county board of equalization for an adjustment this year. The deadline for filing an appeal is Jan. 18, 2011.
Paul Bancroft is a managing partner in the Tucson, Ariz. law firm of Bancroft, Susa & Galloway, the Nevada and Arizona member of American Property Tax Counsel, the national affiliation of property tax attorneys. He can be reached at [email protected].